In the past I do a lot of Azure Governance workshops. One part of this workshops are the high availabilty options in Azure. This article descripe the different SLAs for VM workloads in Azure. Often I get an ask about the SLA level and the requirements. In this discussion many people are confused about the difference of Availability Set and Availability Zone and how this compares to the SLA. The new feature about the Proximitiy Placement Groups comes into play to make the confusing complete. This article descripes the differences between these features.
Contents
Overview
From the high availability aspect it is really important to know the differences about Availability Sets and Availability Zones, to avoid downtimes and get well planned workloads in Azure.
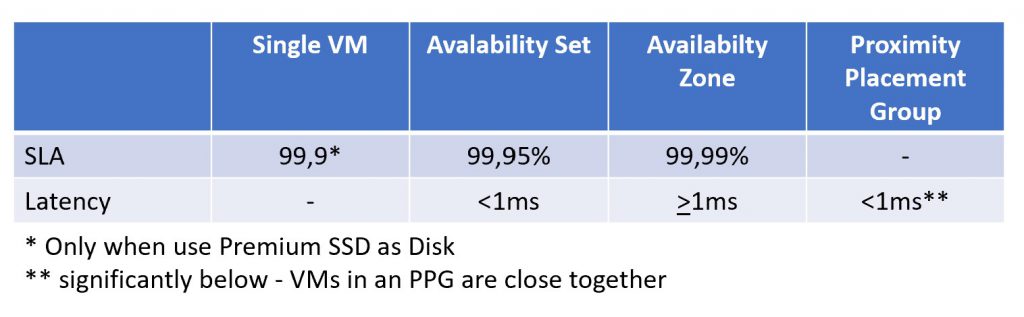
Keep in mind, when deploying an Azure VM as a Single VM there are only an SLA when the VM use Premium Storage like Premium SSD. Provision an single VM on Standard HDD/SSD on Azure results into an VM without an SLA level. Only when a Single VM use Premium SSD for the disks, the VM get an SLA of 99,9%.
Availability Set
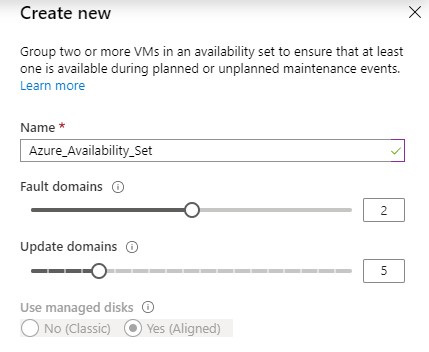
Creating an Availability Set is easy via the Portal. The creating can be done in the step of the VM creation process. With the creation of an Availability Set, Azure creates a group for Azure VMs. This VMs must be from the same category. When provisioning Azure VMs and places this VMs in an Availability Set, Azure place this VMs on different Update and Fault domains.
Update and Fault Domains
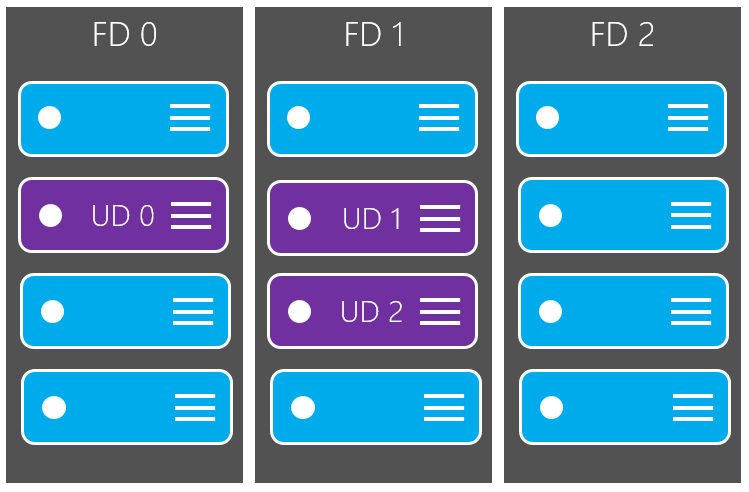
Using an Availability Set for Azure VMs results in placement of Azure VMs in different Update and Fault Domains. A Fault Domain in Azure means an Hardware Rack. Every Fault Domain has it´s own power supply and network connectivity.
Update Domains indicates that underlying Hardware of an Azure VM can be rebooted without causes downtime for the workloads, because the second VM runs on a different Update Domain. Per default Azure creates 5 Update domains – meaning placing the 6th VM in the same AS get in the same Update domain like the 1th VM.
Recommendation
Using Availability Set for workloads and group workloads in the same Availability Set. Like Webserver in an AS_Webserver and Middletier VMs in AS_Middletier and so on. Availability Set is best practice for placing Domaincontroller as example in Azure.
SLA
To use Availability Set for an Azure VM, all VMs must be from the same Size. Azure VMs they are part of an Availability Set get an SLA of 99,95%.
Availability Zone
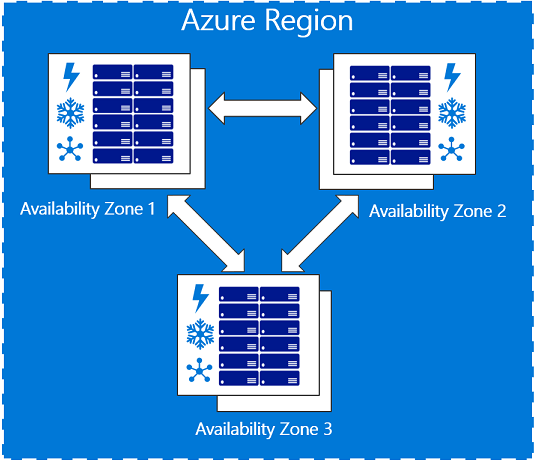
Availability Zones was introduced with the Microsoft Ignite 2017 to achieve an higher SLA for workloads in Azure. Availability Zones creates a group in an Azure region spanned over different datacenter in this region.
Availability Sets and Zones are free of charge, payment is only for the enrolled VMs. With this in mind, many customers think only to use Availability Zone to get an higher SLA. But this single view forget many other facts. One key fact is the difference about latency for workloads they are running on the enrolled VMs.
Keep in mind, VMs in an Availability Set runs in the same datacenter in different fire zones. VMs in Availability Zones run in different datacenter in the same region. This causes higher response time between the VMs. For VMs inside an Availability Set there is an response under 1ms, VMs inside an Availability Zones has an response time about 1ms.
Recommendation
Availability Zones are really useful for workloads they need high availability in every case, such as SQL Databases, Web Applications and more. But consider the higher latency.
SLA
Provision Azure VMs in an Availability Zone results in an SLA about 99,99% for the VMs inside the Availability Zone.
Proximity Placement Groups
Hopefully, the difference between Availability Set and Availability Zone are now clear. With the latency perspective there comes a new feature into play. Microsoft introduces Proximity Placement Groups in July 2019 and the service is GA since December 2019.
Proximity Placement Groups are a service to minimize the latency between VMs to an absolut minimum. PPG are indend for workloads such as SAP architecture in Azure and all other workloads they are sensitive for latency.
Summary
To deploy Azure VMs with SLA Level, there are a need for some basic knowledege. Deploying single VMs on Azure wihtout using Premium Storage results in an VM without an SLA.
For group of VMs they are deliver the same workload, such as Webservices, Domainservices and so on, use Availability Sets and Availability Zones to achive an higher SLA compare to Single VMs. But keep in mind Availability Zone are not a remedy for every workloads, because the placing on different datacenter in the same region results in an higher latency between the VMs.
Pricing
Availability Sets are free of charge, billing is only for the VMs inside the Availability Sets.
Availability Zones are free of charge right now. But additional inter-Availability Zone VM-to-VM data transfer charges will come. Billing will begin April 1. 2020. Thanks Daniel Neumann for the hint.
Links
- Azure Blog – Introducing Availability Zones
- Azure Blog – Introducing Proximity Placement Groups
- Microsoft Docs – Manage Availabilty
- Microsoft Docs – What are Availability Zones
- Microsoft Docs – Availability Zones billing
- Microsoft Docs – Configure multiple VMs in an AS
- Azure – SLA for Virtual Machines
- Azure Blog – Azure Availability Zones now available
- Azure Blog – GA of Proximity Placement Groups